Yup! You have your Linux server or desktop installed, you have been enjoying this setup and suddenly you need to know how many network adapters are installed.
You probably also want to know which of these adapters is connected to the internet, please follow through.
First, you should run the command below on the terminal
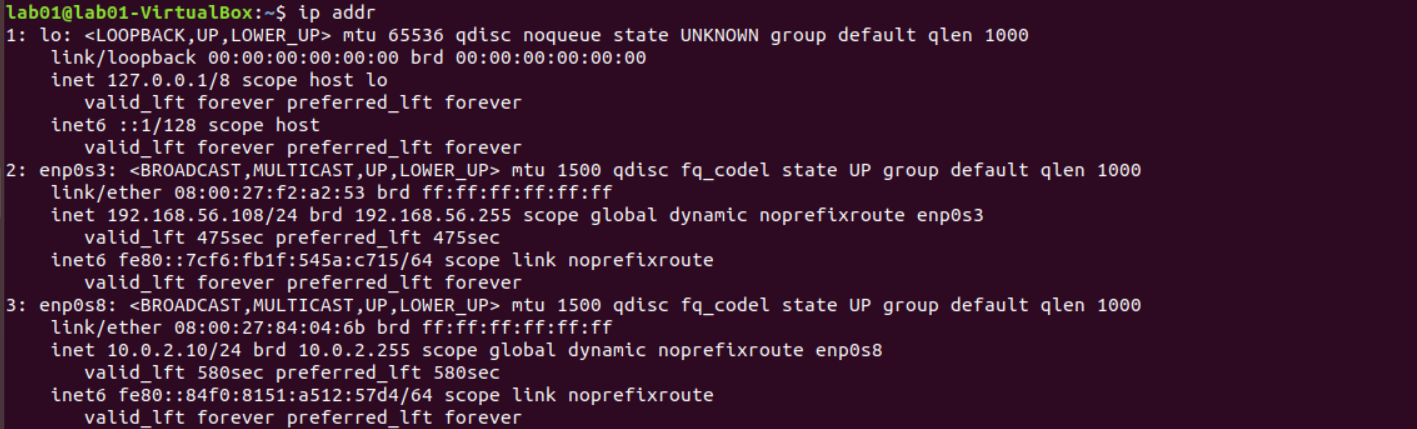
ip addr
TL; DR: There are 2 network adapters here, “enp0s3” is my internet network adapter because it has an IP address from my internet gateway/router/MiFi. The IP address pattern gives this information.it begins with 192.x.x.x. Also "epn0s8" is the local network adapter which allows connections within an ethernet,
This output is quite verbose. Let’s dissect it in a bit.
Firstly, we can observe items 1, 2 and 3. It is worth mentioning that item 1 is not an adapter, it is synonymous with the local network.
Item 1 is labelled as “lo:”, this means that details in this section have to do with your localhost. Internal network setting of your system. This is very evident from the fact that the IPV4 address on the third line is the common loopback address aka 127.0.0.1. Whatever happens on this network interface is never leaving your workstation unless others are configured.
Item 2 is labelled as "enp03s". It has an IPV4 address with the pattern as 192.168.x.x. most of the time when you connect your workstation to a network device, the network device will assign an IP to your workstation, this IP will have a pattern as such. If you have multiple devices attached to the same network device(e.g MiFi/WiFi/Router/Modem), only the last parts of the IP will change(not more than the last 2 octets).
This is the adapter that has access to external network/devices, which may also have access to internet services.
Item 3 is labelled as "enp0s8", and the IP assigned is 10.0.2.10. This adapter only has access to other local workstations within the same ethernet. Also, this means that the network interface is not using an automatic DHCP or the DHCP is configured to use this range of IP (e.g., 10.0.x.x). usually, this interface will not have access to the internet.
In some cases, it will be able to send out internet traffic but will not be reachable from outside the local network.
The beauty of Linux is its flexibility, you might encounter situations where a NAT is configured for this IP on the firewall. The NAT could enable smooth inbound and outbound traffic from the internet.
DECIPHERED? Maybe, let's know. Use the comment section to pass your questions and feedback. You can also send private messages.
Thanks for reading, see you later in another mind-opening Linux/System Admin tutorial.
Comments
Post a Comment